Making Billions, Heading For Trillions
Elon Musk is one of the most influential and talked-about figures of the 21st century. Where did he start, and how did he successfully build a billion-dollar life? Check it out in this article.

It All Started In Africa
Born in South Africa, Elon Musk was remarkably curious about the world around him. However, he faced bullying at school and often found solace in books and technology. When his parents divorced, he turned to science fiction and computers—something that would contribute to his future success.
 Joseph Ayerle, Wikimedia Commons
Joseph Ayerle, Wikimedia Commons
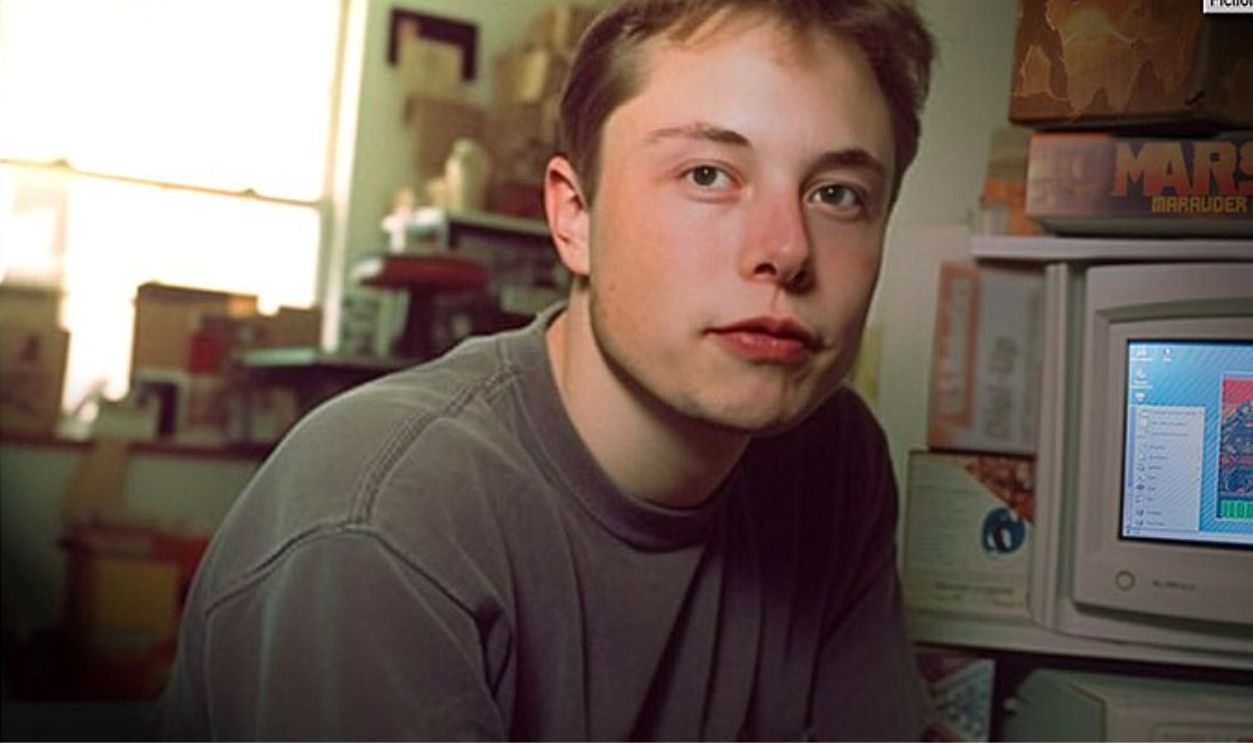
He Taught Himself Programming
Young Elon used a manual to discover the secrets of programming on his Commodore VIC-20. By the age of 12, he developed his first game, Blastar, a space-themed video game. He sold it to a computer magazine for a whopping $500.
 Port of "Blastar" by Elon Musk by Jim Gerrie
Port of "Blastar" by Elon Musk by Jim Gerrie
Then Became A Nightclub Owner
After moving to Canada to attend Queen’s University, Musk worked odd jobs to support himself. Then, he moved to the University of Pennsylvania, where he pursued two degrees in physics and economics. He rented a 10-bedroom house and turned it into a makeshift nightclub to help cover living expenses.
 Justin Pacheco, Wikimedia Commons
Justin Pacheco, Wikimedia Commons
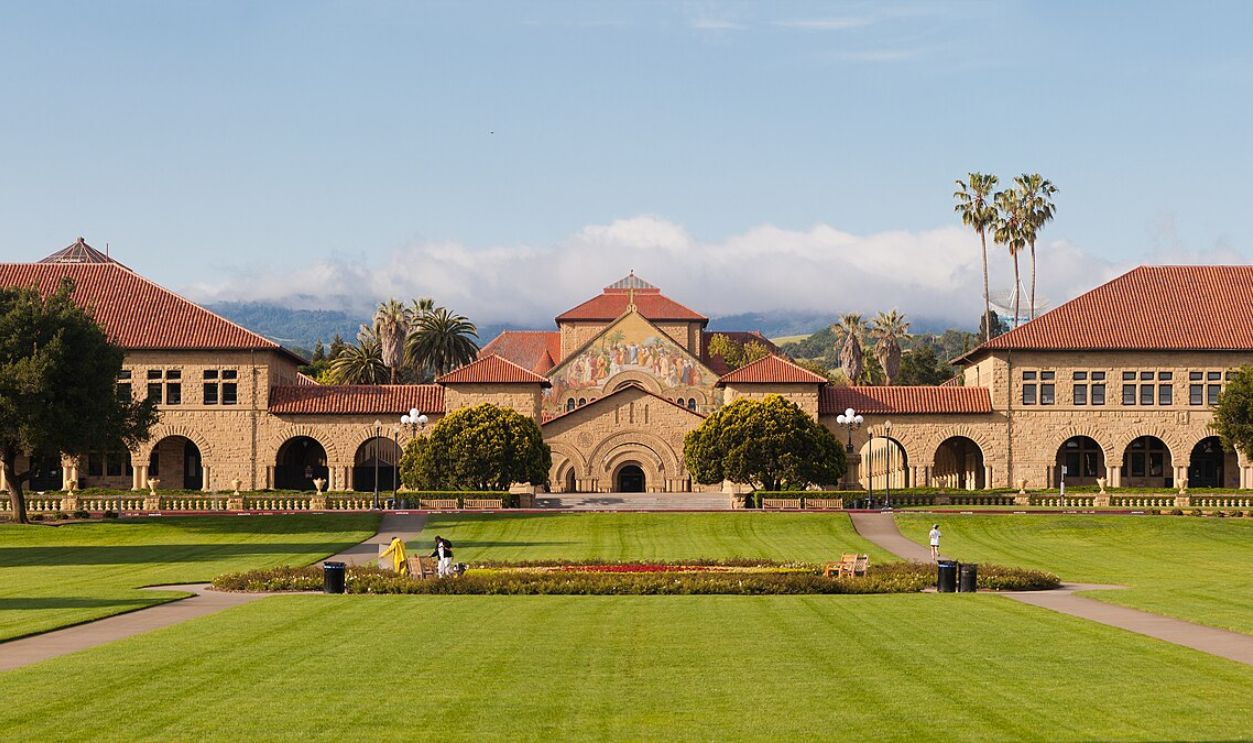
He’s A Stanford Dropout
After completing his degrees, Musk moved to California to pursue a Ph.D. in applied physics and materials science at Stanford University. However, he dropped out two days later to focus on the internet boom of the 1990s and the opportunities it presented.
 King of Hearts, CC BY-SA 3.0,Wikimedia Commons
King of Hearts, CC BY-SA 3.0,Wikimedia Commons
To Become A Business Owner
This bold decision marked the beginning of his first major venture, Zip2, and set the stage for a career defined by risk-taking. It was a software company that provided business directories and maps to newspapers, a concept that laid the groundwork for what we now know as online city guides.
 Elon Musk on Zip2 and the Internet (1988) by PodiumVC
Elon Musk on Zip2 and the Internet (1988) by PodiumVC
His First Big Exit
Although Musk and his mates struggled, Compaq Computer Corporation acquired Zip2 for $305 million in 1999, which marked his first major financial success. At just 28 years old, he knew how to profit from his investments at the right time.
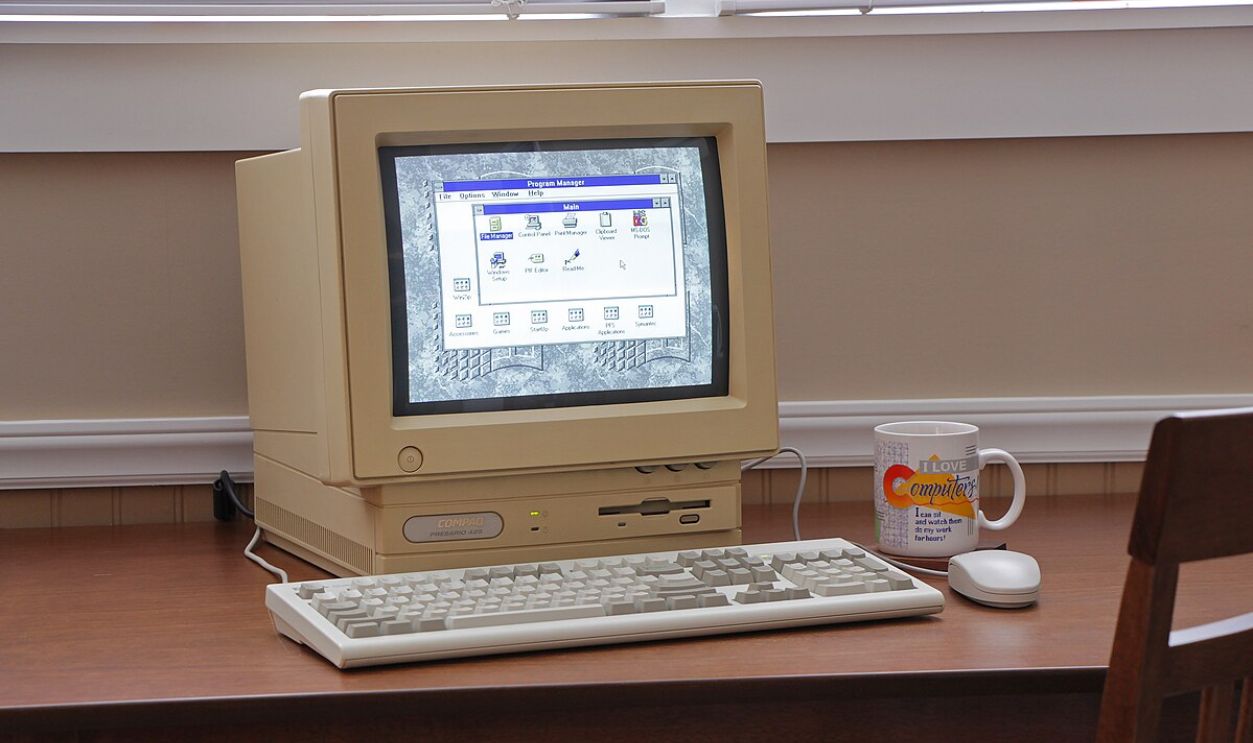 phreakindee, CC0, Wikimedia Commons
phreakindee, CC0, Wikimedia Commons
His Share Funded X.com
With newfound wealth and confidence, Musk turned his attention to the financial sector. In 1999, he co-founded X.com, an online payment and financial services company. X.com allowed users to send money via email, which was one of the first fintech innovations.
 Wcamp9, CC BY 4.0 , Wikimedia Commons
Wcamp9, CC BY 4.0 , Wikimedia Commons
PayPal Was A Hit
X.com merged with Confinity, a company that had developed a money transfer service called PayPal. PayPal’s success attracted the attention of e-commerce giant eBay, which acquired it for $1.5 billion in stock—another significant milestone in Elon Musk’s career.
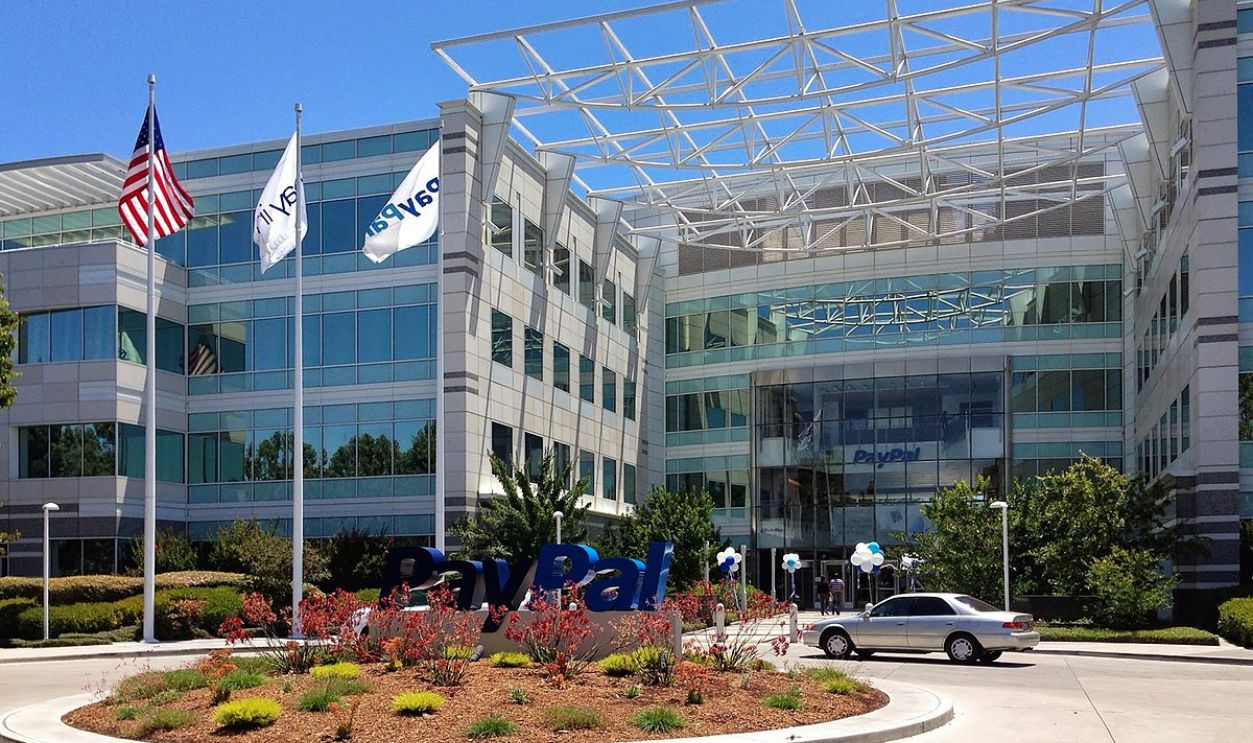 Sagar Savla, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Sagar Savla, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
He Turned To The Sky
After the PayPal sale, Musk turned his attention to space exploration. In 2002, he founded SpaceX, which aimed to reduce the cost of space travel and help humans live on other planets. Despite challenges, Falcon 1, the first privately developed liquid-fueled rocket, successfully reached orbit.
 Bruno Sanchez-Andrade Nuño, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Bruno Sanchez-Andrade Nuño, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
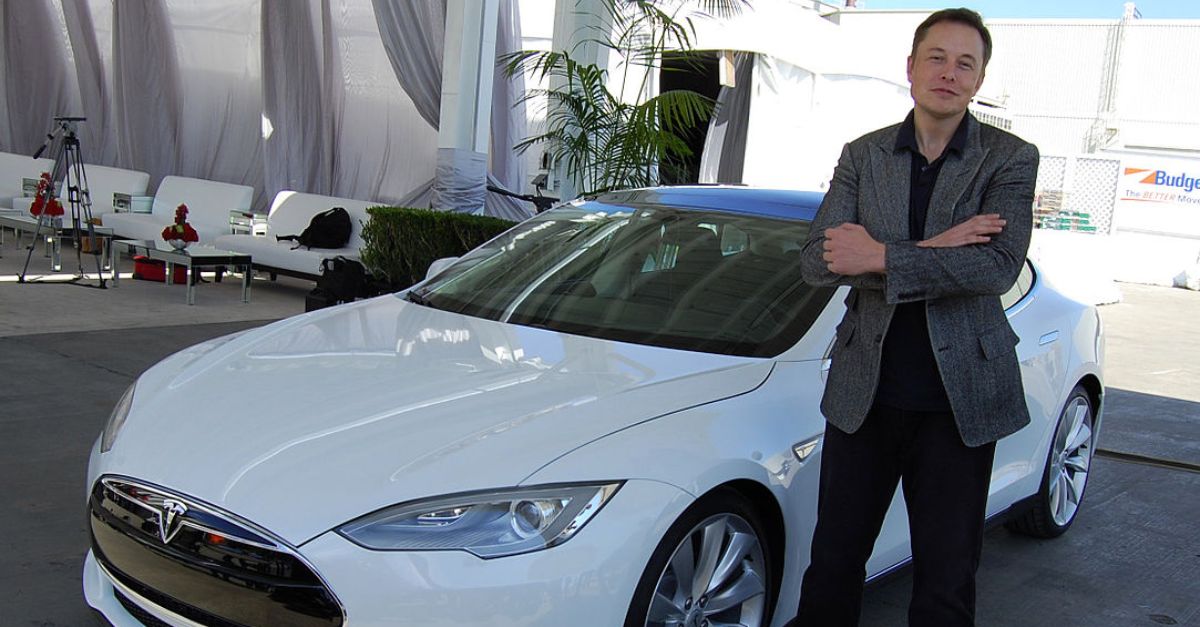
He Entered The Electric Vehicle Market
On the ground, Musk joined Tesla Motors to become chairman of the board. Tesla's first car, the Roadster, was released in 2008 and demonstrated that EVs could be desirable. Musk's commitment to innovation set the stage for the company to become a global leader in EVs.
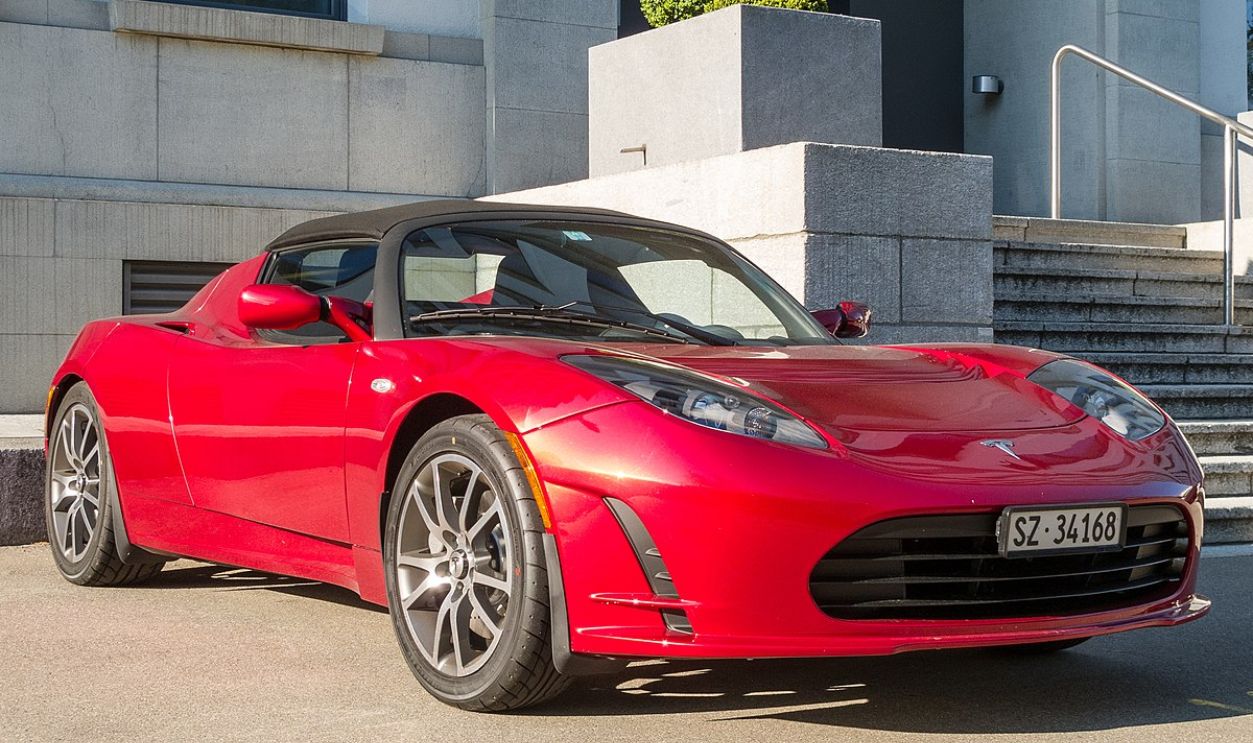 JoachimKohlerBremen, CC BY-SA 4.0 , Wikimedia Commons
JoachimKohlerBremen, CC BY-SA 4.0 , Wikimedia Commons
But He Was About To Deal With Bankruptcy
While Musk's ventures showed promise, Tesla and SpaceX faced severe financial challenges in the late 2000s. By 2008, Tesla was on the brink of bankruptcy due to production delays and limited capital, while SpaceX had failed three consecutive rocket launches.
 U.S. Air Force / Trevor Cokley, Wikimedia Commons
U.S. Air Force / Trevor Cokley, Wikimedia Commons
He Had To Make A Tough Decision
Musk faced an agonizing decision: he could either save one company or try to save both. In a high-stakes move, he split his remaining funds between the two companies. Tesla managed to secure emergency funding, and SpaceX launched its fourth rocket in 2008.
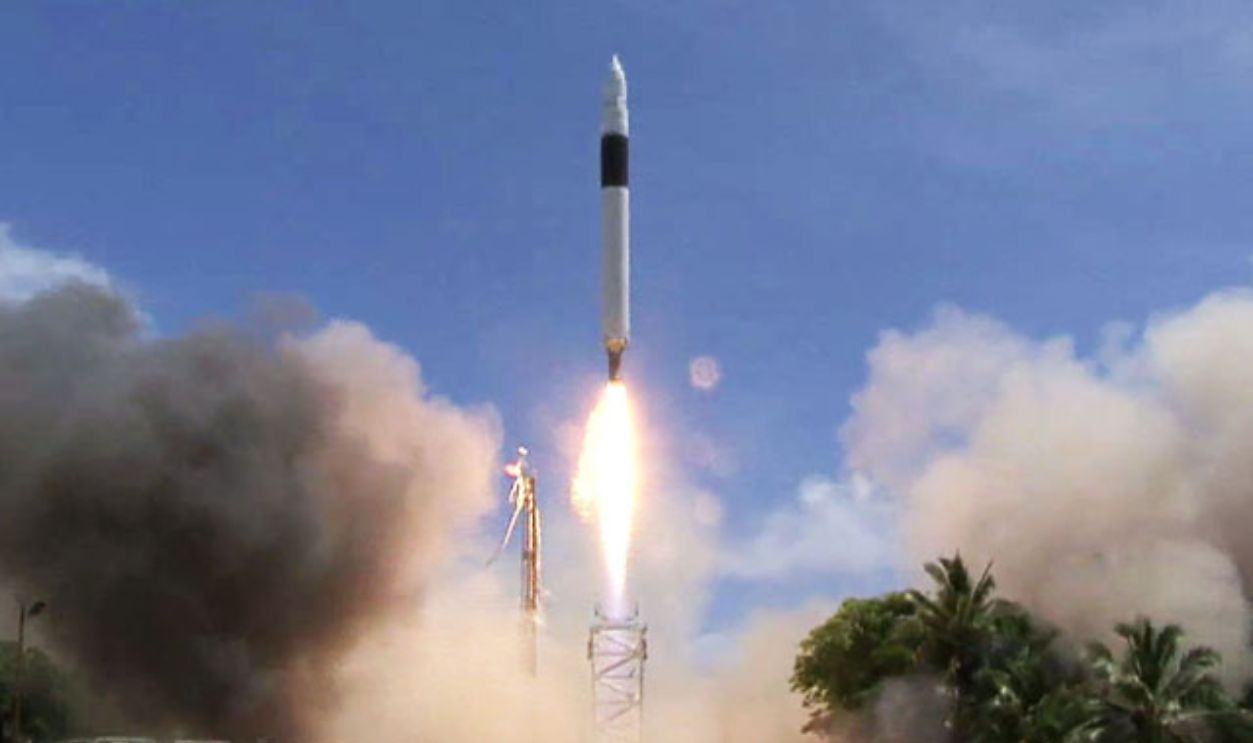 SpaceX, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
SpaceX, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
SpaceX Partnered With NASA
SpaceX caught the attention of NASA, which was looking for private companies to support its space missions. In 2008, SpaceX was awarded a $1.6 billion contract through NASA's Commercial Resupply Services program to transport cargo to the International Space Station.
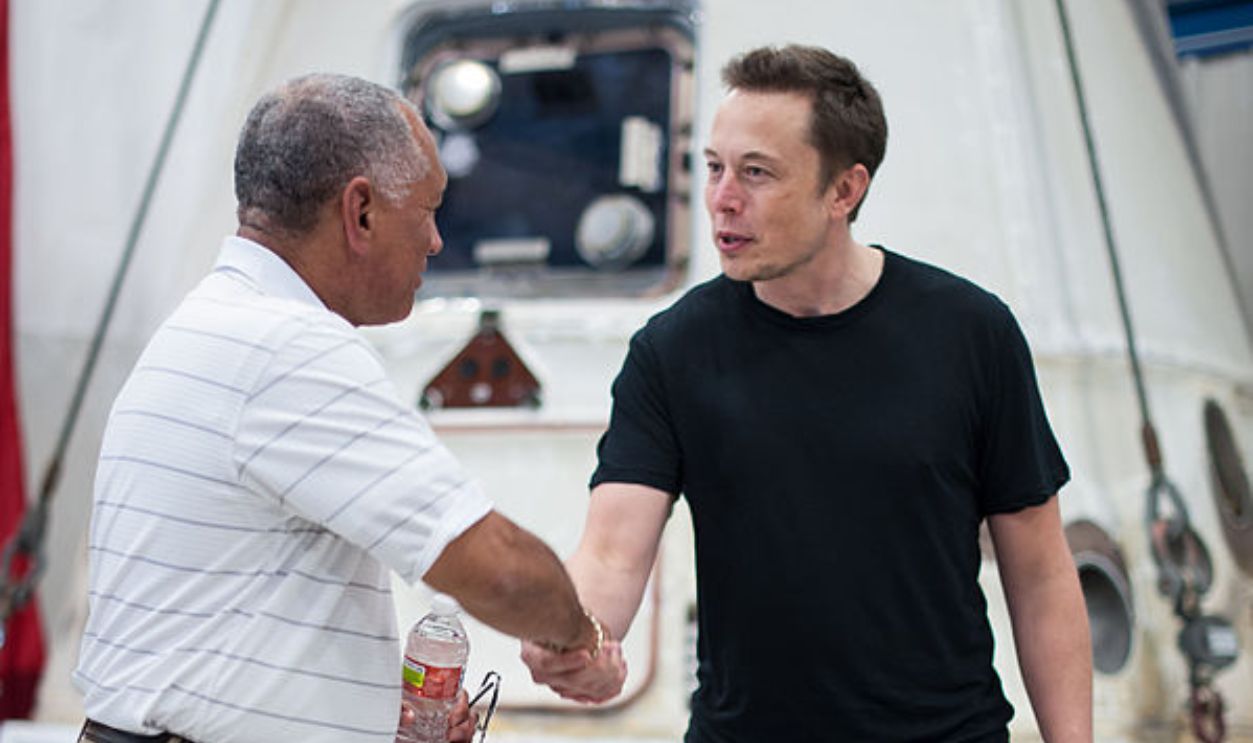 Bill Ingalls, Wikimedia Commons
Bill Ingalls, Wikimedia Commons
A New Approach To Space Travel
Over the years, SpaceX has completed numerous successful resupply missions to the ISS and has developed rockets like the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy. Thanks to its innovative approach to reusable rockets that reduced launch costs, SpaceX changed space exploration.
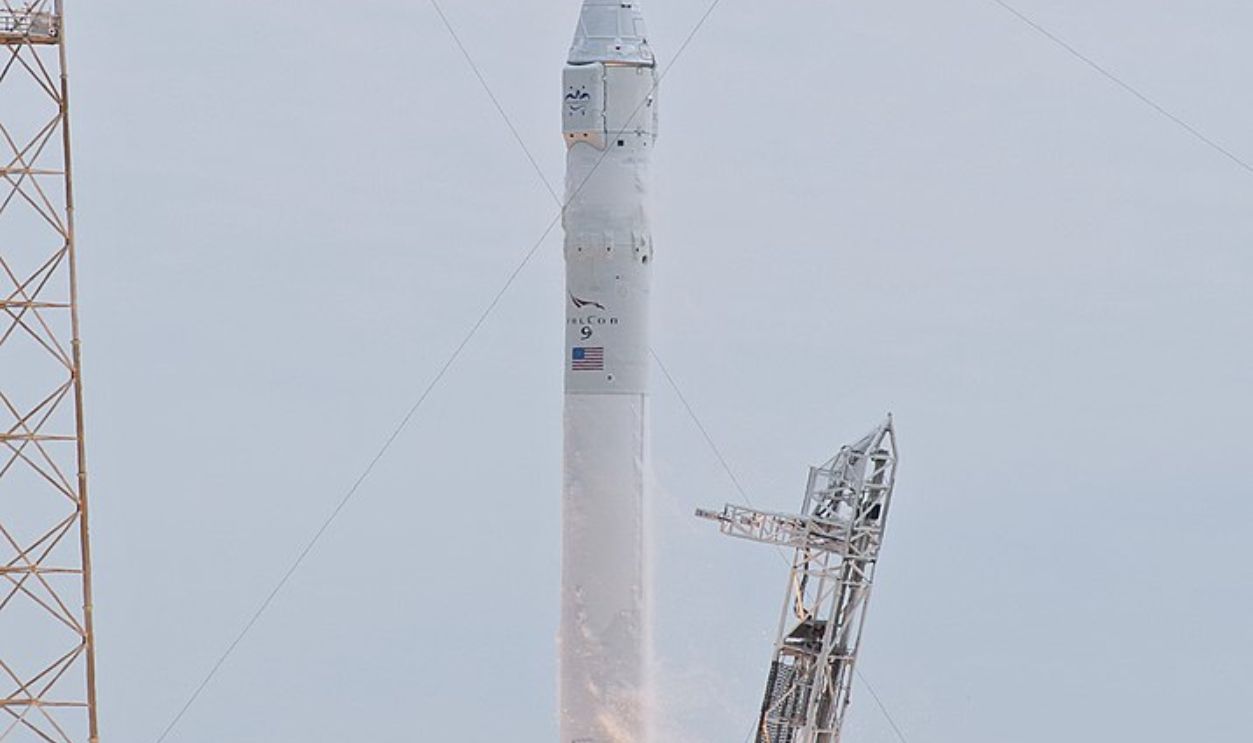 Tony Gray and Robert Murray, Wikimedia Commons
Tony Gray and Robert Murray, Wikimedia Commons
Success On The Ground, Too
At the same time, Tesla launched the Model S, a luxury electric sedan that showed the potential of electric vehicles. The Model S was praised for its sleek design and impressive performance, including a range that far surpassed previous EVs, and it won multiple awards.
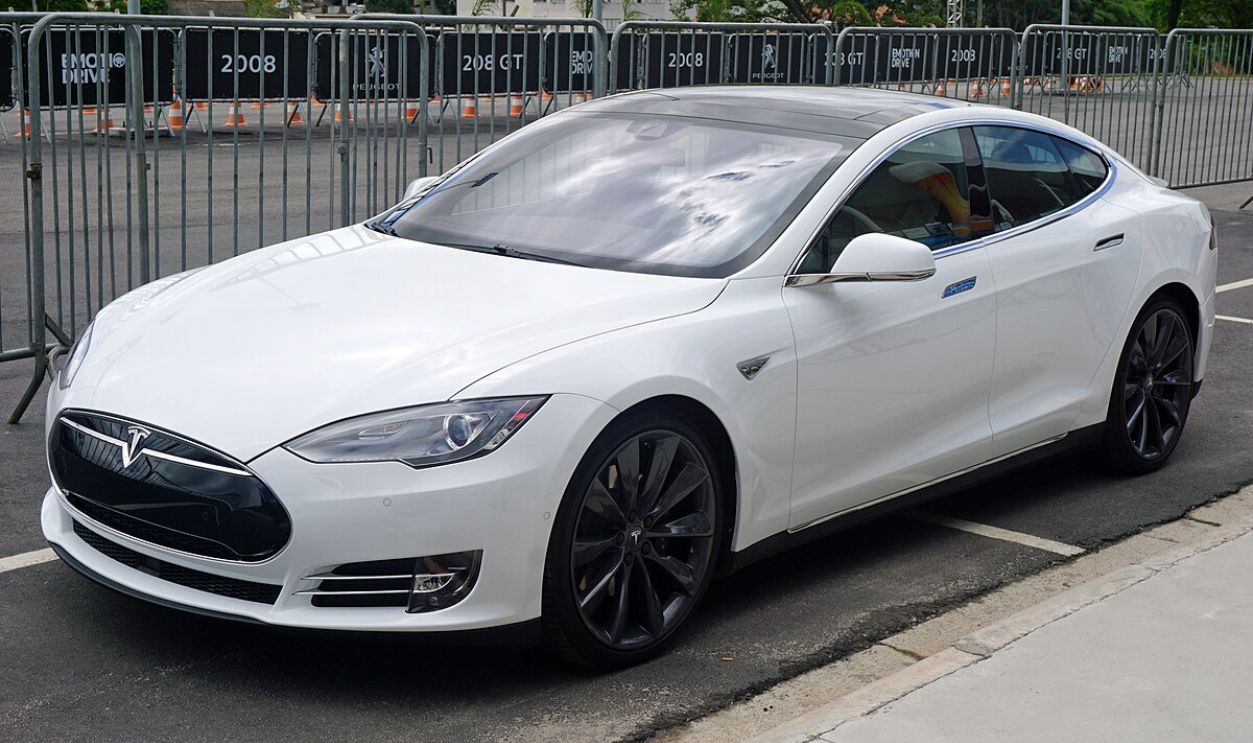 Mariordo , CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Mariordo , CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
He Didn’t Stop There
You’d think Musk has had enough? In 2016, he founded The Boring Company, a tunnel construction and infrastructure company aimed at solving urban traffic congestion. He wanted to create underground transportation systems that could move vehicles and pedestrians efficiently using electric sleds. Sounds like a futuristic dream!
 Steve Jurvetson, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Steve Jurvetson, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
And Another One
Musk also discussed the concept of the Hyperloop, a high-speed system that uses pressurized tubes and magnetic levitation to propel passenger pods. The Hyperloop can reduce travel times between cities while providing an energy-efficient alternative to traditional transportation, but it’s still under development.
 Okras, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Okras, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
No Longer A Niche Product
With Model 3, Tesla made EVs more accessible to the mass market while maintaining Tesla's high performance and technology standards. Despite early production issues, it became one of the best-selling electric cars globally, further solidifying Tesla's dominance in eco-friendly transportation.
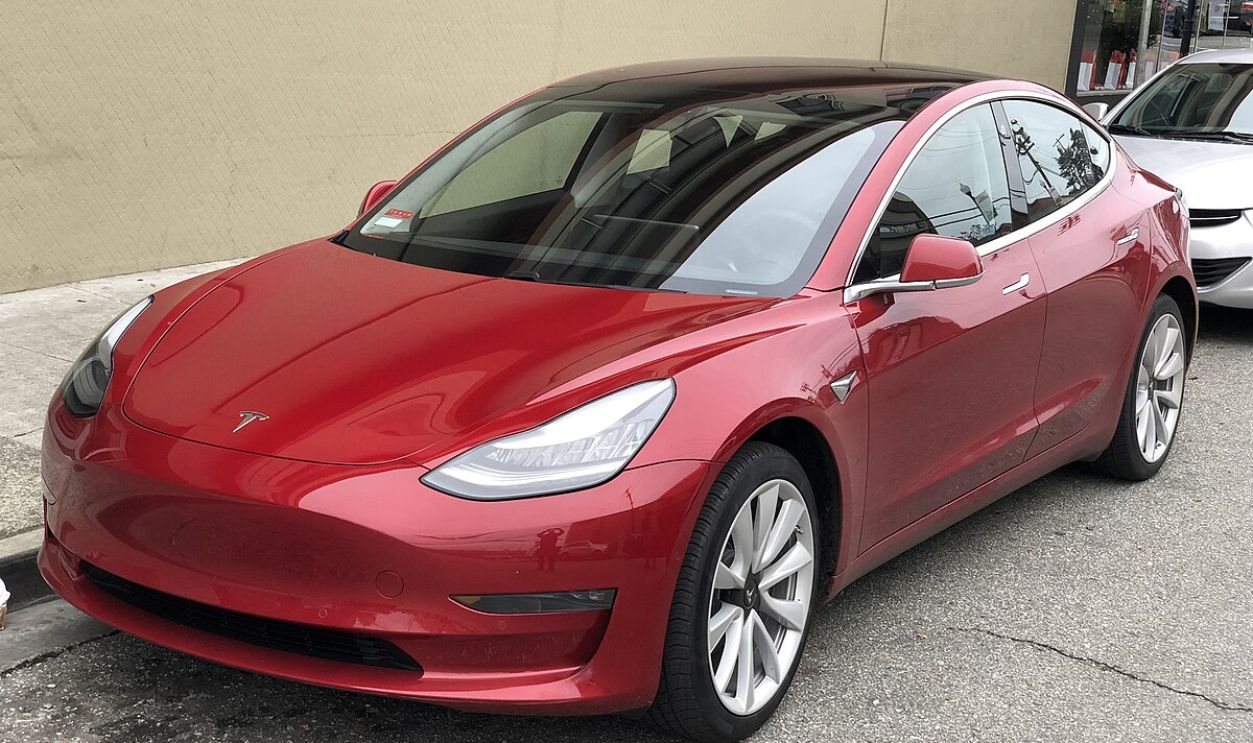 Carlquinn, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Carlquinn, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
He Left His Mark
Capable of carrying enormous payloads into orbit, SpaceX launched Falcon Heavy to compete with traditional aerospace giants like Boeing and Lockheed Martin. In typical Musk fashion, the launch also had a quirky twist—a Tesla Roadster, complete with a mannequin astronaut named "Starman," was sent into space as a test payload.
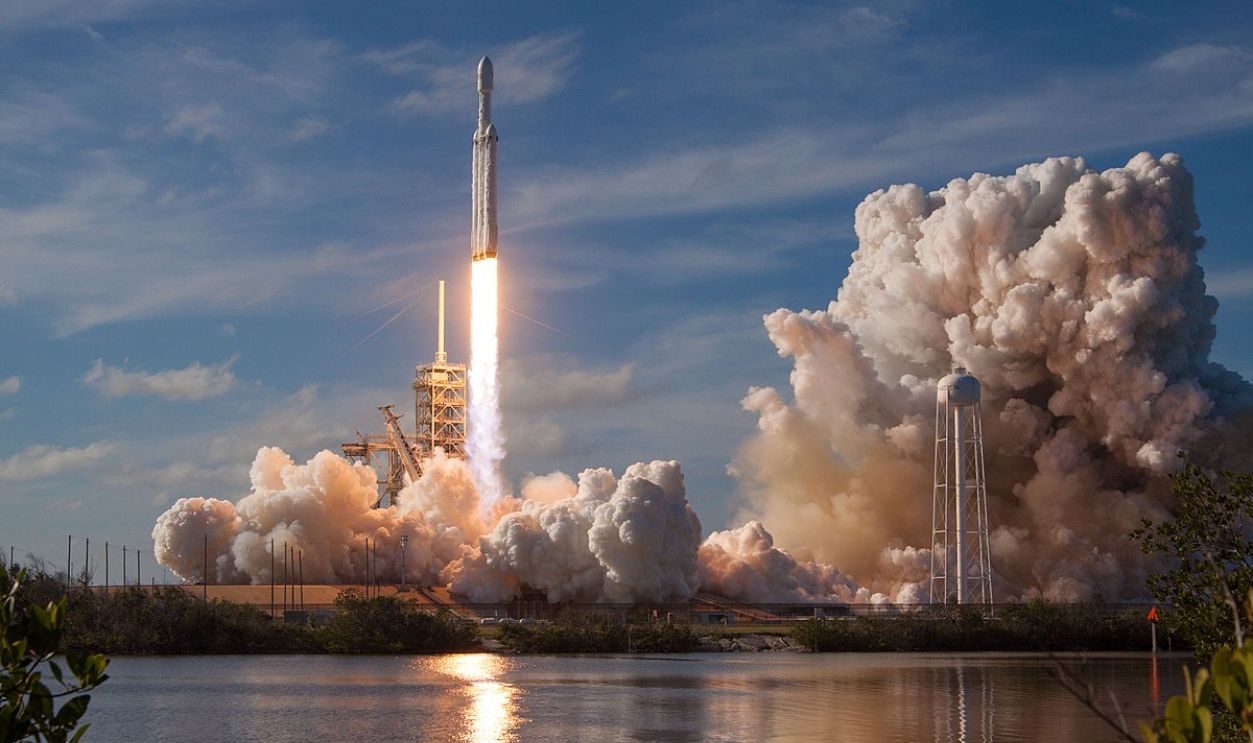 SpaceX, CC0, Wikimedia Commons
SpaceX, CC0, Wikimedia Commons
He Expanded Global Internet Access
Musk and SpaceX launched Starlink as a satellite constellation project aimed at providing high-speed internet to underserved and remote regions worldwide in 2019. Starlink relies on thousands of small satellites in low orbit to deliver broadband internet to areas lacking reliable connectivity.
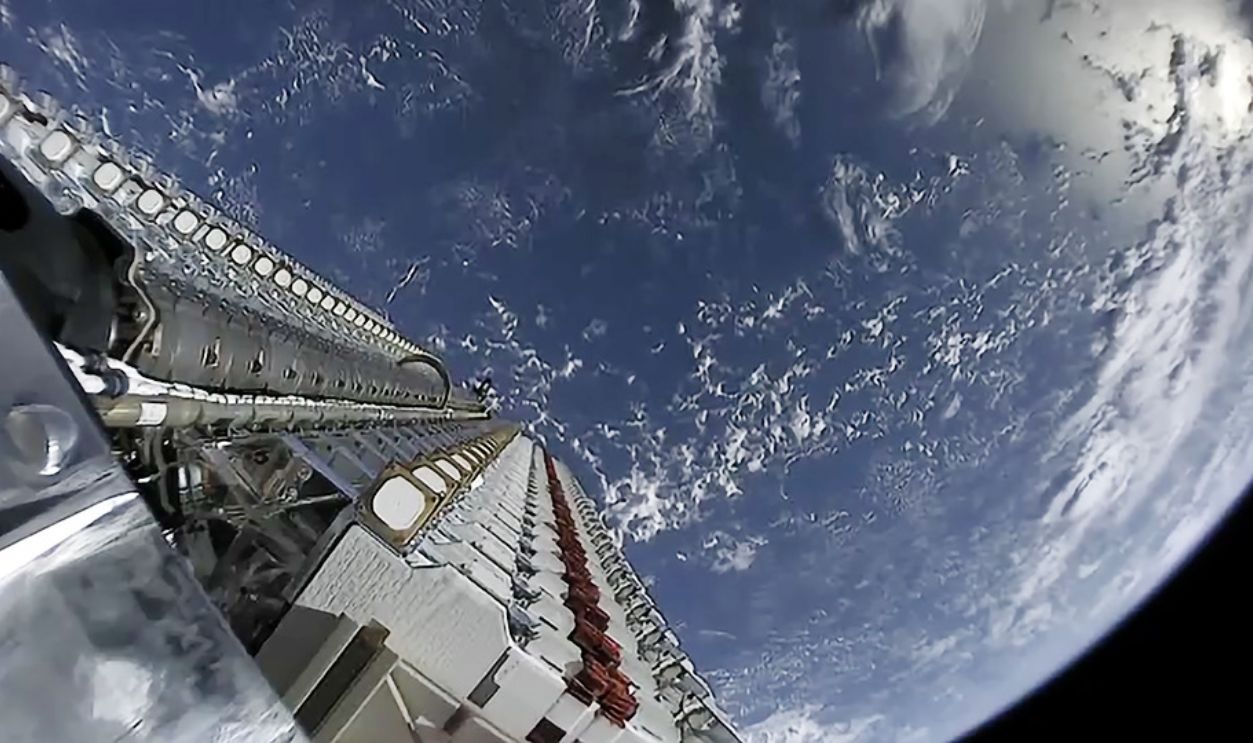 Official SpaceX Photos, CC0, Wikimedia Commons
Official SpaceX Photos, CC0, Wikimedia Commons
Then, It Was Time For Our Brains
Elon Musk then co-founded Neuralink in 2016 to explore the interface between the human brain and machines. The company has been working on implantable devices that connect the brain with external systems, potentially allowing paralyzed individuals to control computers or prosthetics with their thoughts.
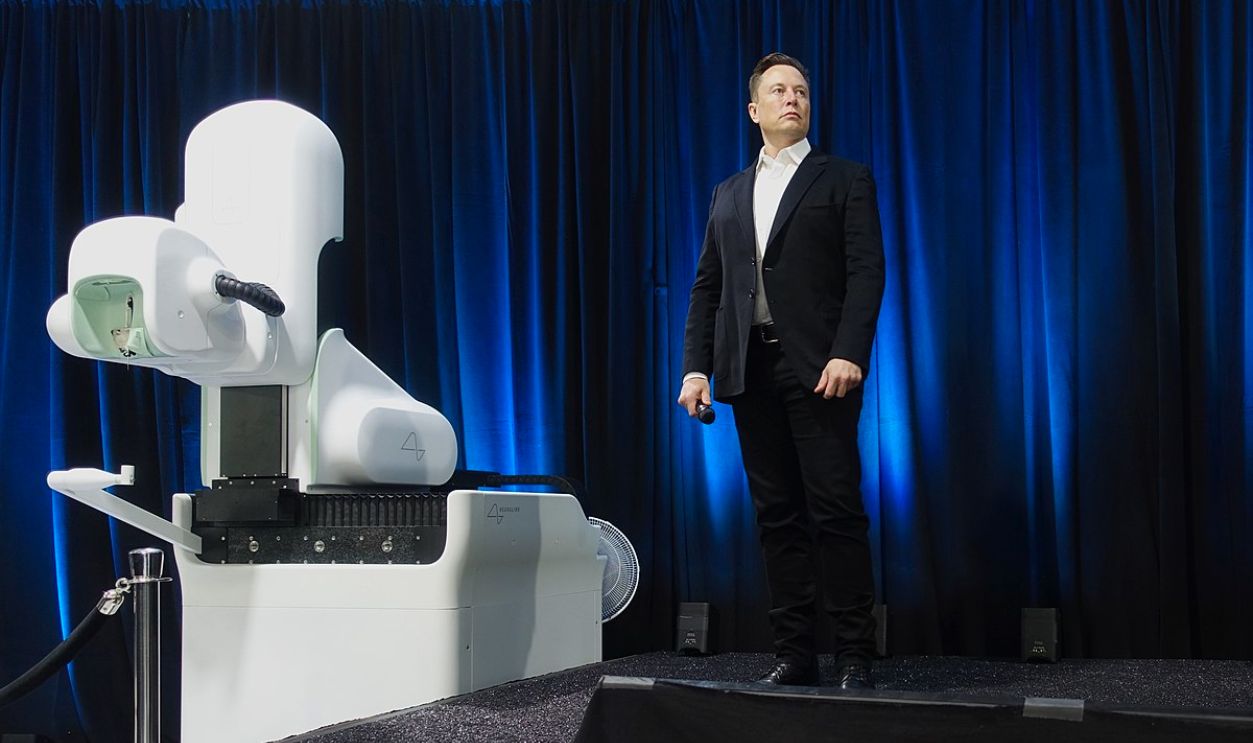 Steve Jurvetson, CC BY 2.0 , Wikimedia Commons
Steve Jurvetson, CC BY 2.0 , Wikimedia Commons
He Knows Sustainable Energy Is The Answer
Tesla acquired SolarCity, a solar energy company co-founded by Musk's cousins, for $2.6 billion. He wanted to integrate SolarCity's solar panel technology with Tesla's energy storage products to create a holistic renewable energy solution to create solar roofs, Powerwalls, and Powerpacks.
 BrokenSphere, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
BrokenSphere, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Musk Became The Richest Person In The World
By 2021, Musk's wealth surged to unprecedented levels to become the richest person in the world. The rapid rise in Tesla's stock price and SpaceX's increasing valuation catapulted Musk's net worth past $300 billion. Unlike traditional billionaires whose wealth comes from diverse investments, Musk's fortune is tied to his companies.
 The Royal Society, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Royal Society, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
He Wanted To Own The Virtual Space
Musk has had an interest in protecting free speech. So, he acquired Twitter after a public battle with its owners. After taking control, Musk implemented significant and controversial changes, including mass layoffs, the introduction of a subscription model, and rebranding the platform as "X".
He Still Holds His Title
Elon Musk is currently worth more than $400 billion to become one of the richest people alive. He’s working on improving his xAI as he offers Grok the chatbox to all X users. We can’t help but question how long it would take him to reach a trillion dollars?
 NORAD and USNORTHCOM Public Affairs, Wikimedia Commons
NORAD and USNORTHCOM Public Affairs, Wikimedia Commons








